Wrist Arthrits
Overview
Wrist arthritis, a common form of arthritis, affects millions of people worldwide. It involves inflammation of one or more of the joints in the wrist, leading to pain, swelling, and a decrease in wrist movement. The condition can be debilitating, making simple tasks such as opening a jar or typing on a keyboard difficult.
Types
Wrist arthritis generally falls into two categories:
1. Osteoarthritis: Also known as wear-and-tear arthritis, it predominantly occurs in the elderly as joint cartilage gradually erodes over time.
2. Rheumatoid arthritis: This is a chronic autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues, including the joints in the wrists.
Causes
While the exact cause of wrist arthritis is unknown, certain factors increase the risk of developing the condition. These include:
– Age: Being older increases the chance of developing arthritis
– Gender: Women are more likely to develop wrist arthritis than men
– Overuse: Repetitive motions or injuries that stress the wrist joint
– Genetics: Certain genes associated with rheumatoid arthritis
Symptoms
Common symptoms of wrist arthritis include:
– Persistent joint pain
– Swelling in the wrist
– Difficulty moving the wrist or hand
– Weakness in the hand
Less commonly, some patients may experience flare-ups where symptoms intensify suddenly.
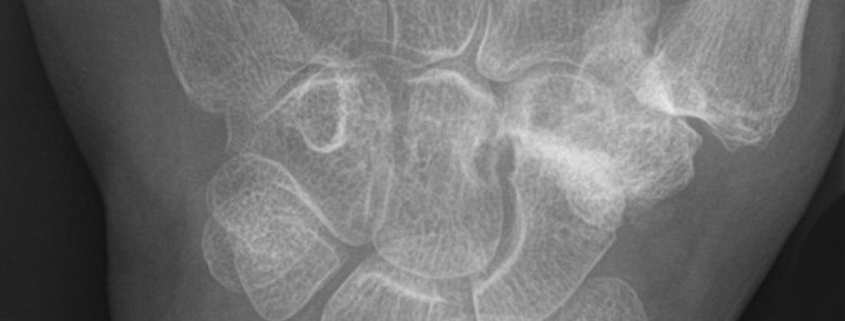
Diagnosis
Wrist arthritis is usually diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. Your doctor may also require lab tests to determine if the arthritis is due to an autoimmune disorder.
Treatment Options
While wrist arthritis is not curable, there are several treatment measures to manage the condition’s symptoms. These may include:
– Medication: Over-the-counter and prescription drugs help reduce pain and inflammation
- Physical Therapy: Exercises improve flexibility and strength in the wrist
– Splinting: Wearing a splint or wrist brace provides support and eases discomfort
– Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement or joint fusion may be useful
Living With Wrist Arthritis
Living with wrist arthritis involves diligent self-care including:
– Regular exercise: Builds strength and improves joint flexibility
– Weight management: A healthy weight reduces stress on the joints
– Heat or cold therapy: Applying heat or cold reduces pain and inflammation
– Stress reduction: Mind-body techniques, such as meditation or yoga, may offer relief
When to Seek Help
While occasional wrist discomfort is not uncommon, seek immediate medical attention if you experience persistent wrist pain, noticeable swelling or redness in the wrist, or if you have difficulty moving your wrist or hand. Early treatment can help prevent irreversible joint damage.
Following this advice, you can manage your wrist arthritis effectively and improve your quality of life. Remember, consulting a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan is essential for dealing with any health concern.
