Fibromyalgia: Navigating the Complexities of Chronic Pain
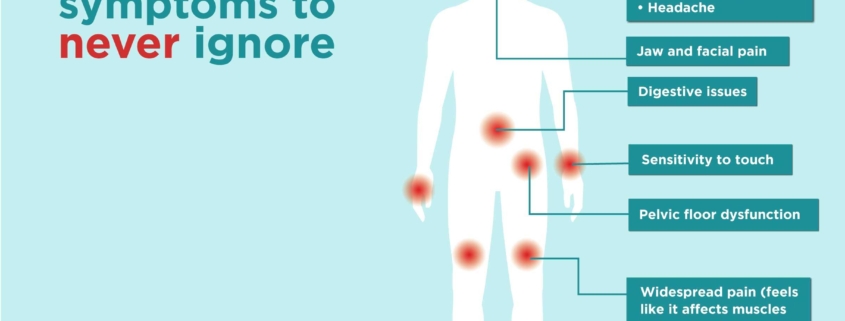
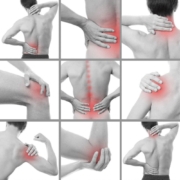
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue, sleep, memory, and mood issues. While not directly impacting your bones or joints, fibromyalgia significantly affects how your muscles and tissues feel, making everyday activities challenging. Understanding this complex condition is the first step toward managing it and improving your quality of life.
What Causes Fibromyalgia?
The exact cause of fibromyalgia remains unknown, but research suggests several contributing factors:
Genetics: Having a family history of fibromyalgia increases your risk.
Physical or Emotional Trauma: Events like accidents or periods of high stress can trigger the condition.
Infections: Some illnesses may trigger the development of fibromyalgia.
Central Nervous System Sensitivity: People with fibromyalgia may experience pain signals more intensely.
Managing Fibromyalgia: Your Path to Relief
While there’s no cure for fibromyalgia, the good news is that it can be effectively managed. Here are some strategies to help you regain control and live a fuller life:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
Exercise Regularly:
Start slowly with low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling.
Gradually increase the intensity and duration as your body adapts.
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Prioritize Sleep:
Establish a regular sleep schedule and stick to it, even on weekends.
Create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal your body it’s time to sleep.
Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool.
Manage Stress:
Identify your stress triggers and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
Seek support from friends, family, or a therapist.
Eat a Balanced Diet:
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
Limit your intake of sugar, caffeine, and alcohol, which can worsen symptoms.
2. Medical Treatments:
Medications:
Your doctor may prescribe medications to help manage pain, improve sleep, and regulate mood.
Common medications include pain relievers, antidepressants, and anti-seizure drugs.
Physical Therapy:
A physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
They can also provide guidance on posture, body mechanics, and assistive devices.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
CBT is a type of therapy that can help you identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to pain.
It can also teach you coping skills for managing stress, anxiety, and depression.
Taking Charge of Your Health
Living with fibromyalgia can be challenging, but it doesn’t have to control your life. By understanding the condition and taking proactive steps, you can manage your symptoms and improve your overall well-being. Remember, you are not alone. Don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider or support groups for guidance and support on your journey to better health.