Joint Pain 101: A Comprehensive Guide to Common Conditions
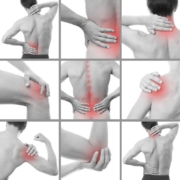
Joint pain can affect anyone, regardless of age or activity level. Understanding the common causes and how to prevent them is crucial for maintaining healthy joints and overall musculoskeletal health. This guide will provide you with actionable information to keep your joints healthy and pain-free.
Why Healthy Joints Matter
Our joints allow us to move freely and enjoy everyday activities. When they’re healthy, we can walk, run, jump, and participate in the things we love. Protecting our joints now can prevent pain and limitations later in life.
Common Causes of Joint Pain
Several conditions can lead to joint pain. Some of the most common include:
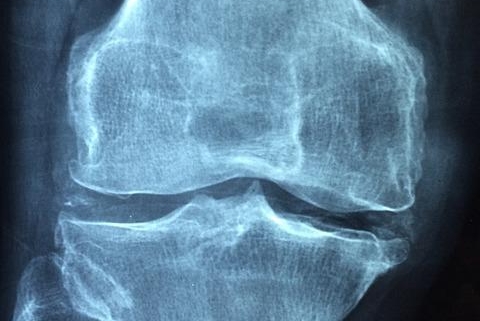
Osteoarthritis: This is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones wears down over time.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: This is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and pain.
Bursitis: This is inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near your joints.
Tendonitis: This is inflammation or irritation of a tendon, the thick fibrous cords that attach muscle to bone.
Injuries: Sprains, strains, and fractures can all cause joint pain.
Preventing Joint Pain: A Proactive Approach
While some joint conditions are unavoidable, many can be prevented or managed through lifestyle choices. Here are some key strategies:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Why it matters: Excess weight puts extra stress on your joints, particularly your knees and hips.
Actionable steps:
Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein.
Engage in regular physical activity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Consult a nutritionist or dietitian for personalized guidance.
2. Exercise Regularly:
Why it matters: Exercise strengthens the muscles surrounding your joints, providing support and stability. It also helps maintain flexibility and range of motion.
Actionable steps:
Choose low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, or walking.
Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle.
Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
Consult a physical therapist for a personalized exercise plan.
3. Practice Proper Posture:
Why it matters: Good posture aligns your body correctly, reducing stress on your joints.
Actionable steps:
Stand tall with your shoulders back and your head held high.
Sit with your back straight and your feet flat on the floor.
Avoid slouching or hunching over.
Take breaks to stretch and move around if you sit for long periods.
4. Use Proper Lifting Techniques:
Why it matters: Lifting heavy objects incorrectly can strain your joints, especially your back.
Actionable steps:
Bend your knees and keep your back straight when lifting.
Hold the object close to your body.
Avoid twisting or jerking movements.
Ask for help if the object is too heavy.
5. Protect Your Joints During Activities:
Why it matters: Certain activities can put extra stress on your joints.
Actionable steps:
Wear supportive shoes that fit properly.
Use protective gear, such as knee pads or wrist guards, when participating in sports or activities that put stress on your joints.
Warm up before exercising and cool down afterward.
Listen to your body and rest when you need to.
6. Manage Existing Conditions:
Why it matters: Managing conditions like diabetes and autoimmune diseases can help protect your joints.
Actionable steps:
Follow your doctor’s recommendations for managing your condition.
Take medications as prescribed.
Attend regular checkups.
Key Takeaways and Additional Resources
Taking care of your joints is essential for maintaining an active and healthy lifestyle. By following these preventative measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing joint pain and improve your overall musculoskeletal health.
For more information on joint health, visit the following resources:
The Arthritis Foundation: www.arthritis.org
* The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons: www.aaos.org
Remember to consult with your doctor or a physical therapist if you experience persistent joint pain. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the best course of treatment for your specific needs.